Pipeline Recovery
Pipeline Recovery is a feature in Conduit through which pipelines that experience certain types of errors are automatically restarted. This document describes how Pipeline Recovery in Conduit works and how it can be configured.
Pipeline Recovery is enabled by default since Conduit v0.12. The feature can be disabled if needed.
Introduction
Most pipeline errors encountered are a result of temporary issues like network interruptions or services being unavailable due to maintenance. It then becomes a matter of how we handle the pipeline.
In most cases, simply retrying is enough to get through transient errors efficiently. This can and should be done by connectors and processors, but that may not always be the case. For Conduit users, this typically means they would need to wait for the connector or processor to be updated. This implies that we need to have in Conduit an automatic mechanism for restarting pipelines that experienced an error.
What triggers pipeline recovery
Any non-fatal error can trigger pipeline recovery. In the context of pipelines, we differentiate between two types of errors: fatal and non-fatal.
Fatal errors are the errors that a pipeline cannot recover from. Two types of errors are fatal by default:
- DLQ threshold exceeded (because the purpose of the DLQ threshold is to stop a pipeline if too many records are nack-ed)
- Processor errors (because processors are usually deterministic, so if a processor failed processing a record once, it will most likely fail processing a record again)
In one of the next versions of Conduit and the Connector SDK, we'll make it possible for connectors to define what errors they consider as fatal.
Non-fatal errors are all the other errors, i.e. errors for which it makes sense to restart a pipeline and retry the data streaming.
Algorithm
Pipeline Recovery restarts a pipeline using a linear backoff algorithm. One
important addition is that Conduit tracks the number of retries over a period of
time configured by the option max-retries-window.
If max-retries has been set, then Conduit will
make sure that there are at most max-retries over any max-retries-window
period of time. In other words, the number of restart attempts is reset to 0
after max-retries-window.
This way, max-retries-window makes sure that we can safely reset the attempts
to 0 even in the following cases:
- When a pipeline has been running long enough. For example, if a pipeline
failed
max-retries - 1times months ago, then it's unexpected that it fails now because of one failure. - When a pipeline is unstable and frequently failing. For example, a pipeline
might experience an error and recover just before
max-retrieshas been reached. It might run for some time more and then fail again. If we're not careful about resettingmax-retries, then the pipeline might enter another recovery cycle very soon, which would be against what a user intended (limiting the number of retries).
Here's a diagram of the algorithm:
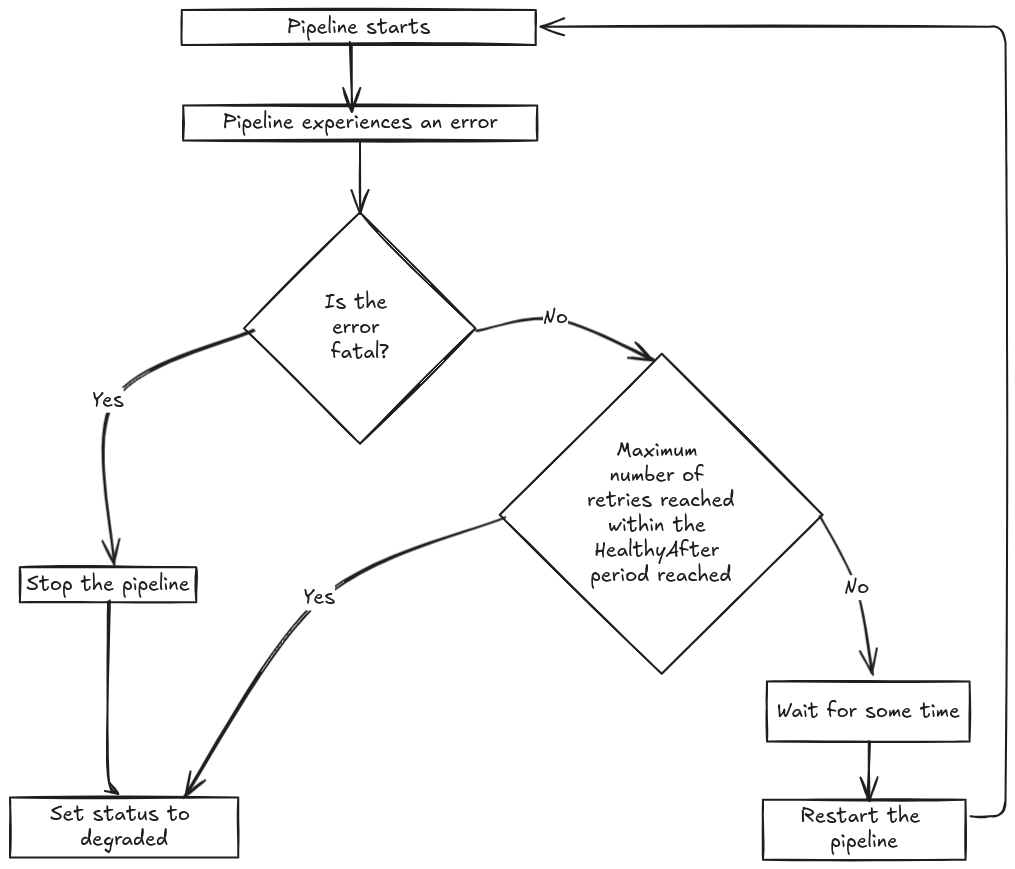
How to disable Pipeline Recovery
To disable Pipeline Recovery, you should set the configuration parameter
pipelines.error-recovery.max-retries to 0. With this, you'll have the
pre-v0.12 behavior, where a pipeline stops and goes into the degraded state
the first time it experiences an error.
Configuration
pipelines.error-recovery.min-delay
- Data Type: Duration
- Required: No
- Default: 1s
- Description: Minimum delay before restarting the pipeline after an error.
pipelines.error-recovery.max-delay
- Data Type: Duration
- Required: No
- Default: 10m
- Description: Maximum delay allowed before restarting the pipeline after an error.
pipelines.error-recovery.backoff-factor
- Data Type: Integer
- Required: No
- Default: 2
- Description: Backoff factor applied to the last delay when recovering from errors.
pipelines.error-recovery.max-retries
- Data Type: Integer
- Required: No
- Default: -1
- Description: Maximum number of retry attempts before the pipeline gives
up. A value of
-1indicates infinite retries.
pipelines.error-recovery.max-retries-window
- Data Type: Duration
- Required: No
- Default: 5m
- Description: No more than
max-retriesare allowed within anymax-retries-windowperiod of time.
Examples
Example 1: Setting a custom max-delay
The conduit.yaml below shows how to set a custom maximum delay before a
pipeline is restarted. By default, max-delay is 10 minutes and here we're
setting it to 10 seconds.
pipelines:
error-recovery:
max-delay: "10s"
If a pipeline experiences an error, the delays between restarts will be as follows:
- Attempt 1: 1s
- Attempt 2: 2s
- Attempt 3: 4s
- Attempt 4: 8s
- Attempt 5: 10s
- Attempt 6: 10s
- ...
- Attempt N: 10s
Example 2: Setting a custom max-retries and max-retries-window
The conduit.yaml below shows how to limit the number of pipeline restarts to
3 (by default, the number of retries isn't limited). It also sets the
max-retries-window to 10 minutes (default value is 5 minutes).
pipelines:
error-recovery:
max-retries: "2"
max-retries-window: "10m"
Below, we'll explain different scenarios with failing pipelines using the same Conduit configuration.
Scenario 1: Maximum number of retries reached
15:00 Pipeline starts. 15:10 Pipeline experiences an error (source system unavailable). 15:10 Pipeline is restarted (retry #1).
15:11 Pipeline experiences an error again. 15:11 Pipeline is restarted (retry #2).
15:15 Pipeline experiences an error again.
15:15 Pipeline has been restarted 2 times (max-retries) over the last 10
minutes (max-retries-window). No more retries are allowed, hence the pipeline stops
and its status is set to degraded.
Scenario 2: Number of retries reset after some time
15:00 Pipeline starts.
15:10 Pipeline experiences an error (source system unavailable). 15:10 Pipeline is restarted (retry #1).
15:11 Pipeline experiences an error again. 15:11 Pipeline is restarted (retry #2).
15:20 Internally, Conduit increments the number of available retries by 1,
because 10 minutes (max-retries-window) since the first retry have passed.
15:35 Pipeline experiences an error again.
15:35 Pipeline is restarted because we didn't restart 2 times (max-retries) over the last 10
minutes (max-retries-window).